Share this
3 Reasons Why 3D Printing Filaments are so Expensive
by 3devo on Mar 3, 2019 9:39:00 AM

Why are Filaments Expensive and What can You Do About It?
When buying filaments for your 3D printer, a common question may cross your mind – Why are these things so expensive? After all, it’s only a piece of plastic, right?
Yes, but there is more to 3D filaments than what meets the eye! We invite you to explore some of the factors that affect the price of a filament. First, we’ll immerse ourselves in the basics of filaments and what it costs to get them from the manufacturer to your home. In addition, we will offer several secrets that will help you reduce the cost of filaments without sacrificing quality.
1. Material
3D printer filaments are made of various polymers, the technical name for various ‘plastics.’ Polymers are chains of repeating segments of molecules. The most common plastics for 3D filament include ABS (a copolymer of acrylonitrile, butylene, and styrene) and PLA (polylactic acid). We invite you to learn more about them in the following article. Never less, 3D printing may utilize almost any polymer if it has the following properties.
- Thermoplasticity
It may be remolded when heated – Essential for 3D printing. - Ductility
It can be “stretched out” when heated – Though it must not “leak” once it has been set. - Durability
It’s durable when cooled down – This property can be enhanced or compromised based on your project.
The quality of a filament is determined by these properties. Additionally, you may require other special abilities for a specific product, such as flexibility (nylon), weather resistance (ASA), or outright strength (polycarbonate). In the graphic below, you can see which materials are superheroes in their respective categories.
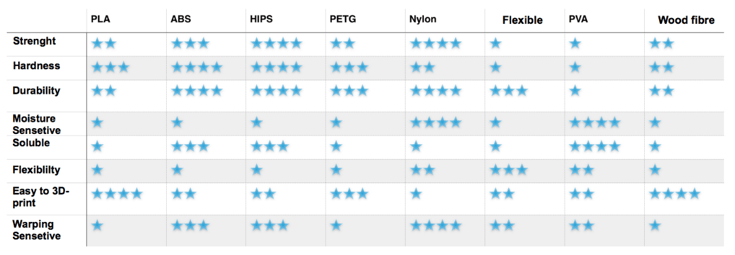
Types of filaments and their properties
The cost of a polymer plays the leading role in the overall price of the filament. Each comes from a different source and requires various techniques to prepare.
The quality of a polymer can also be reduced by impurities, which are common when it is prepared by cheaper methods. We can testify to this through our own experience. Even though we’ve been pleased to find cheap filaments on some e-commerce websites, we’ve always ended up with low-quality products that leaked, cracked, smelled terrible, etc.
This illustrates the bad results with low-quality filaments
2. Additives
Let’s talk about a less-mentioned but important part of filaments – the additives! The color of filaments alone suggests that they contain something more than just pure plastic. It is fascinating to explore the variety of enhancements that can be included in a filament and their effect on its price.
The most common additive is a dye. Dyes vary wildly in quality – factors such as color, solubility, UV resistance, and toxicity can play a role in their price. This is the case especially for fluorescent dyes which glow in dark or UV active dyes which glow under UV light.
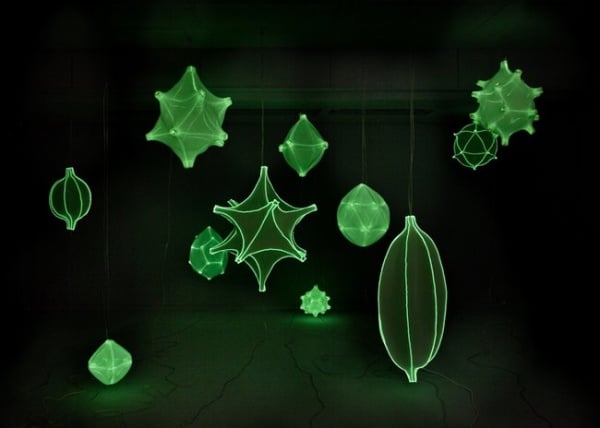

3D Printed Ornaments made from filament with UV active dyes.
Additives can also improve the physical properties of the product. An important example is hardness, which can vary wildly even when considering a single polymer type. This is achieved by adding only small amounts of a necessary additive. But it’s by far not the only property that we can introduce!
Other common additives include flame retardants and autoxidizing agents. The small amount of additives does not impact the stability of the polymer, yet it expands the possible applications of 3D printed products. How cool is that?!

3. Processing, Packaging, And a Niche Market
Let’s look at a less technical topic, which is an issue of both quality and quantity. The processing of polymers into filaments is not necessarily expensive, but it requires special equipment to achieve their uniform dimensions. You may have already found that out the hard way since cheap filaments often end up getting stuck in the printer. The use of expensive specialized equipment necessary for precise extrusion will be reflected in the price.
After extrusion, the filament is cut, packaged, and sold, not in bulk but in single threads. It is necessary to wind every filament onto a plastic (or metal) spindle, called spooling. The spool adds to the weight quite a bit, increasing the fuel required to ship them. It is also inefficient since the rolled-up filaments contain a lot of air. This contributes to the price as well.
We must also account for the size of the market. This is the concept known as the rule of supply and demand. For example, 3D printing is a fast-growing but still niche market. This means that there aren’t many filament manufacturers, especially ones who would sell high-quality products. The demand is increasing, but the production is expensive and low in volume – think of Tesla cars as another example. Thus, the manufacturers can ask for more money than other polymer products, such as plastic spoons.
Tips – How To Reduce The Cost of a Filament
From the reasons we have given, it may seem that compromising on the price of a filament will most likely result in a bitter surprise – and you would be right! Still, there are ways to get around this. So here is a brief overview of the top 5 tips to lower 3D printing costs.
- Buying in bulk is always cheaper than by single spools. You may buy multicolor sets or simply order a wholesale package of filaments.
- Read reviews, recommendations, and compare prices. Thanks to the internet, we have all the information at our disposal!
- Make sure to plan your project thoroughly. Not only that you will not overpay for unnecessarily expensive polymers, but you will end up using less.
- Consider extruding your own 3D filaments from granulates. As seen in the table below, filaments are far more expensive than the granulates they are made from.
- Recycle your products. This requires specialized equipment that reduces plastic products to granulate.
| MATERIAL | FILAMENT PRICE/USD PER KG | GRANULATE PRICE/USD PER KG |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | $25 | $5 |
| PLA | $25 | $5 |
| ASA | $45 | $4 |
| Nylon | $110 | $10 |
| Flexible | $110 | $10 |
(Comparison of popular filament and granulate prices can be found here)

Conclusion
Material, additives, and production costs all add to the final market value. But don’t worry; we have also given you several ways to reduce the cost of your 3D printing operation! Still, there is so much more to 3D printing! Be sure to check out further articles on our blog to learn more about specific types of filaments, extruders, and recycling.
Share this
- November 2025 (1)
- October 2025 (1)
- March 2025 (1)
- January 2025 (1)
- December 2024 (2)
- November 2024 (2)
- October 2024 (4)
- September 2024 (2)
- August 2024 (3)
- July 2024 (6)
- June 2024 (3)
- May 2024 (2)
- April 2024 (1)
- March 2024 (1)
- January 2024 (1)
- November 2023 (2)
- October 2023 (5)
- September 2023 (2)
- August 2023 (1)
- July 2023 (1)
- May 2023 (1)
- December 2022 (2)
- June 2022 (1)
- May 2022 (2)
- April 2022 (2)
- March 2022 (6)
- February 2022 (2)
- January 2022 (3)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (3)
- October 2021 (2)
- September 2021 (3)
- August 2021 (3)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (1)
- March 2021 (1)
- October 2020 (1)
- June 2020 (1)
- May 2020 (1)
- April 2020 (4)
- November 2019 (1)
- July 2019 (2)
- June 2019 (1)
- May 2019 (1)
- March 2019 (1)
- November 2018 (1)
- September 2018 (1)
- January 2018 (1)
- October 2017 (1)
- September 2017 (1)
- July 2017 (1)
- June 2017 (1)
- May 2017 (1)
- January 2017 (1)
- December 2016 (3)
- November 2016 (2)
- October 2016 (1)
- May 2016 (2)
- August 2015 (2)
- July 2015 (1)