Share this
Polystyrene: Versatility & Limitations in Thermoplastics
by 3devo on Sep 24, 2021 4:25:00 PM

Introduction
Polystyrene (PS) is a widely used thermoplastic with a fascinating history and numerous applications. This blog explores polystyrene's characteristics, uses, advantages, and disadvantages, shedding light on its environmental impact and alternative possibilities. Let's delve into the world of polystyrene and discover what makes it so popular yet controversial.
What is Polystyrene?
Polystyrene, a clear, hard, and rather brittle thermoplastic, has a long history dating back to 1839, when it was discovered by Eduard Simon. It then evolved over the years. After about 80 years later, macromolecules were discovered when styrol was heated via a chain reaction thanks to German organic chemist Hermann Staudinger. Eventually, this led to the substance receiving its present name, polystyrene.
Dow Chemical Company then invented a proprietary process to make their trademarked and well-known PS foam product, “styrofoam,” in 1941. Throughout the years, though, the thermoplastic has not been the most favorable in environmental organizations (due to its slow degrading process). It is not hard to deny this fact, as almost anyone can walk outside and see some form of polystyrene trash on the ground.
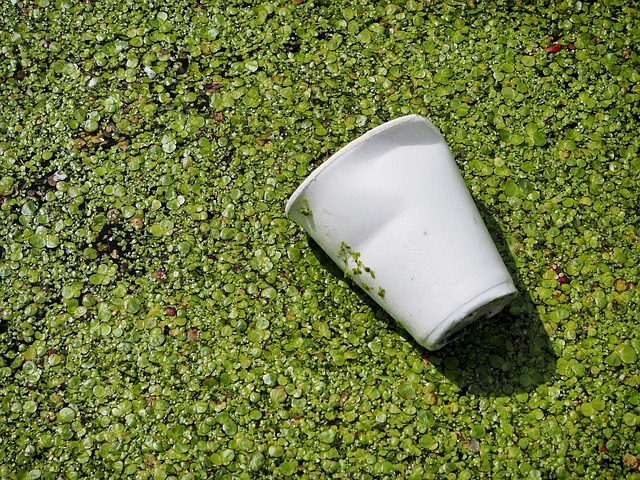

Discarded polystyrene cups, one of the more unpopular uses of the material
To make polystyrene, hydrocarbon fuels are distilled to create lighter groups called “fractions.” Some of which are combined with other catalysts to produce plastics. As a result, the polymerization process creates the PS we all know today. However, it does come in many forms. Much like other plastics, such as PETG and TPU, it also has a whole range of uses.
Common Types and Uses
Beyond its familiar use in cups and packaging, polystyrene finds applications in various forms, including sheet or molded polystyrene used for disposable cutlery, CD cases, and more. Polystyrene foams act as excellent thermal insulators, making them suitable for building insulation, ornamental pillars, and packaging materials. Expanded polystyrene (EPS) stands out as a rigid, tough, closed-cell foam commonly used in trays, plates, bowls, and fish boxes. Extruded polystyrene foam (XPS) also finds its place in crafts and model building.
Sheet or Molded Polystyrene
Objects here are usually created using thermoforming (vacuum forming) or injection molding:
- Disposable plastic cutlery and dinnerware
- CD Cases
- Smoke detector housing
- License plate frames
- Petri dishes
- Test Tubes
CD Case made from polystyrene
Foams
Polystyrene foams are good thermal insulators and are, therefore, often used as:
- Building insulation materials
- Ornamental pillars
- Packaging

The foam type is great for packaging.
Expanded Polystyrene
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a rigid and tough, closed-cell foam. It is usually white and made of pre-expanded beads. Therefore it makes sense to see it in objects like:
- Trays, plates, and bowls
- Fish boxes
How would we ship electronics without it?
Extruded Polystyrene Foam
Extruded polystyrene foam (XPS) consists of closed cells, most commonly seen in crafts and model building.
Common Characteristics
Generally, Polystyrene (PS) is an amorphous, glassy polymer that is generally rigid and relatively inexpensive. Unfilled polystyrene has a sparkle appearance and is often referred to as crystal PS or general-purpose polystyrene (GPPS). High-impact polystyrene grades (HIPS) are produced by adding rubber or butadiene copolymer. Therefore, this increases the toughness and impact strength of the polymer. Other qualities include:
- High surface qualities
- Generally non-toxic and odorless
- Good electric insulator
- Flammable
- Shock-resistance
- Good pressing results
- Ideal for thermoforming
- Polished or mat surface
- Approved for food contact (although some studies have reported “potential health impacts from polystyrene foam food packaging associated with its production)
Advantages and Disadvantages
Polystyrene boasts numerous advantages, such as being inexpensive, readily available, and easy to work with for sanding, gluing, cutting, and painting. On the flip side, its flammability, poor solvent resistance, and brittleness are some of the downsides. Understanding its characteristics helps evaluate its suitability for specific applications.
Pros
- Inexpensive
- Readily available
- White in color
- Easy to sand, glue cut, and paint
Cons
- Flammable but retarded grades are available.
- Inert (i.e., doesn’t react particularly well with either acidic or basic solutions)
- Poor solvent resistance, attacked by many chemicals
- Homopolymers are brittle
- Subject to stress and environmental cracking
- Poor thermal stability
Extruding and 3D Printing
We over at 3devo decided to try out extruding some polystyrene, thanks to the Composer 450 filament maker.
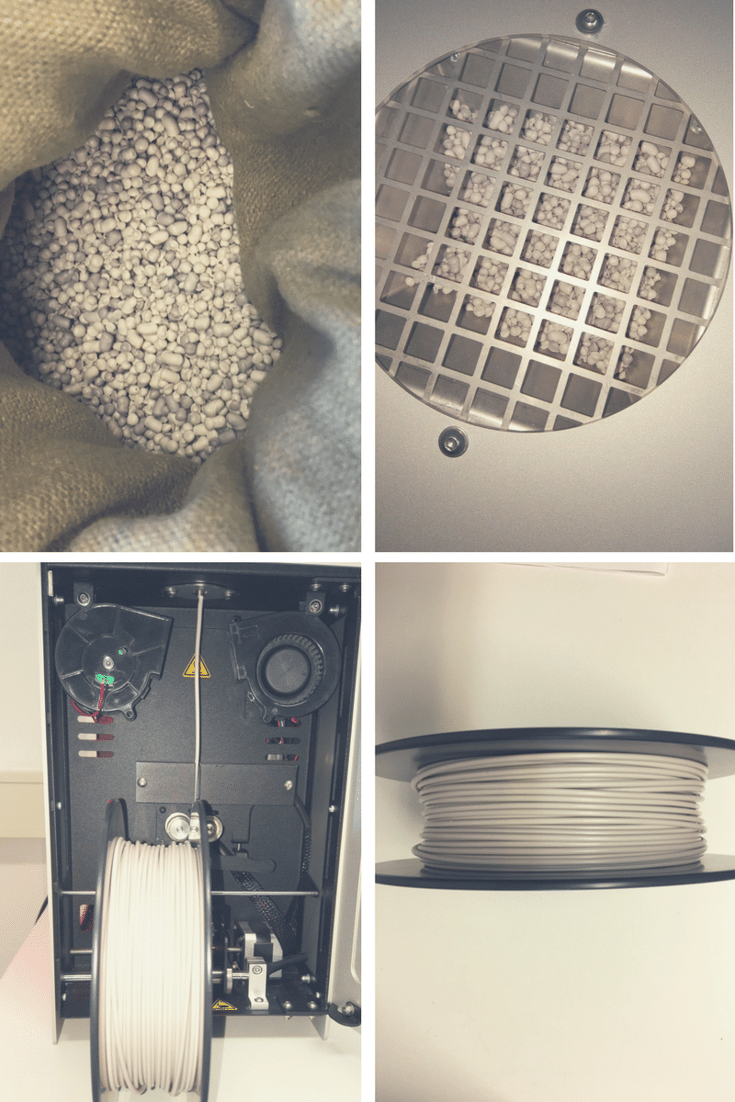

Top Left: PS granules used. Top Right: The PS granules in the hopper. Bottom Left: PS filament being extruded with the Composer 450. Bottom Right: The finished filament!
Extruding the polystyrene filament was a resounding success, thanks to efficient air-cooling via fans, preventing overheating.
For 3D printing with PS, High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) proves excellent. Similar to popular ABS, it offers toughness and durability. Though not the cheapest option, using Limonene as a solvent gives the finished product a slightly lemon-like scent. Careful control of the 3D printer's heater element is crucial to avoid warping when the hot material meets the cooling layer. Printing smaller parts at an appropriate speed can prevent warping issues.
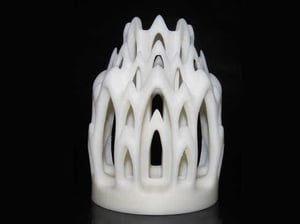
3D Printing with HIPS (via Vexmatech)
Conclusion:
In the end, polystyrene is a very interesting thermoplastic. With quite a range of characteristics and uses, it’s easy to see why it has become so popular. And, although it’s so similar to, say, ABS, its positive qualities, such as its good impact resistance and ease of finishing, make it a strong contender against the other plastics out there.
Ready to make filament with Polystyrene?
Explore the possibilities of creating high-quality filament using the innovative Composer 450 filament maker. Effortlessly extrude Polystyrene and other materials to fuel your creative projects.

Share this
- November 2025 (1)
- October 2025 (1)
- March 2025 (1)
- January 2025 (1)
- December 2024 (2)
- November 2024 (2)
- October 2024 (4)
- September 2024 (2)
- August 2024 (3)
- July 2024 (6)
- June 2024 (3)
- May 2024 (2)
- April 2024 (1)
- March 2024 (1)
- January 2024 (1)
- November 2023 (2)
- October 2023 (5)
- September 2023 (2)
- August 2023 (1)
- July 2023 (1)
- May 2023 (1)
- December 2022 (2)
- June 2022 (1)
- May 2022 (2)
- April 2022 (2)
- March 2022 (6)
- February 2022 (2)
- January 2022 (3)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (3)
- October 2021 (2)
- September 2021 (3)
- August 2021 (3)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (1)
- March 2021 (1)
- October 2020 (1)
- June 2020 (1)
- May 2020 (1)
- April 2020 (4)
- November 2019 (1)
- July 2019 (2)
- June 2019 (1)
- May 2019 (1)
- March 2019 (1)
- November 2018 (1)
- September 2018 (1)
- January 2018 (1)
- October 2017 (1)
- September 2017 (1)
- July 2017 (1)
- June 2017 (1)
- May 2017 (1)
- January 2017 (1)
- December 2016 (3)
- November 2016 (2)
- October 2016 (1)
- May 2016 (2)
- August 2015 (2)
- July 2015 (1)

