Share this
Unleashing the Power of Carbon Fiber Filament: A Comprehensive Guide
by Ellie Pritchard on Jul 24, 2024 3:20:58 PM
Carbon fiber filament has revolutionized the world of 3D printing, bringing unprecedented strength, durability, and versatility to various industries. At 3devo, our Materials Specialists have gained extensive knowledge and experience of working with carbon fiber in our on-site Innovation Lab. In this blog, we’ll delve into the intricacies of Carbon Fiber Filament, its advantages, and the process of extruding this material using a Filament Maker. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a curious newcomer, this guide aims to provide valuable insights and practical tips.
What is Carbon Fiber Filament?
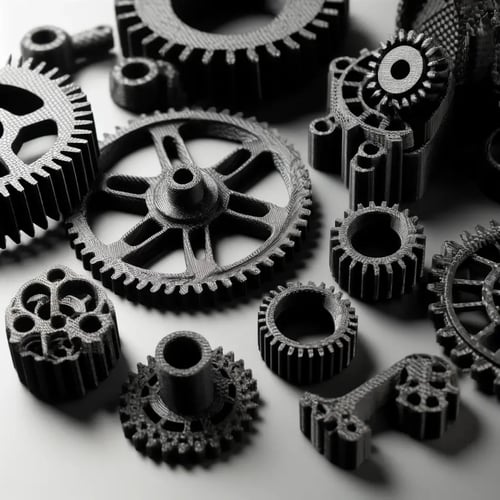

Carbon fiber filament is a composite material made by blending short carbon fibers with a thermoplastic base, such as PLA, ABS, or Nylon. This combination results in a filament that boasts a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent rigidity, and superior thermal and electrical conductivity. The inclusion of carbon fibers enhances the mechanical properties of the filament, making it ideal for high-performance applications in aerospace, automotive, and engineering sectors.
Why Choose Carbon Fiber Filament?
- Enhanced Strength and Stiffness: Carbon fiber filament is significantly stronger and stiffer than standard filaments. This makes it perfect for creating parts that require high structural integrity.
- Lightweight: Despite its strength, carbon fiber filament is incredibly lightweight, which is crucial for applications where reducing weight is essential.
- Heat Resistance: Carbon fiber filament can withstand higher temperatures compared to regular filaments, making it suitable for demanding environments.
- Dimensional Stability: Parts printed with carbon fiber filament exhibit minimal warping and shrinking, ensuring precision and accuracy.
The Filament Extrusion Process
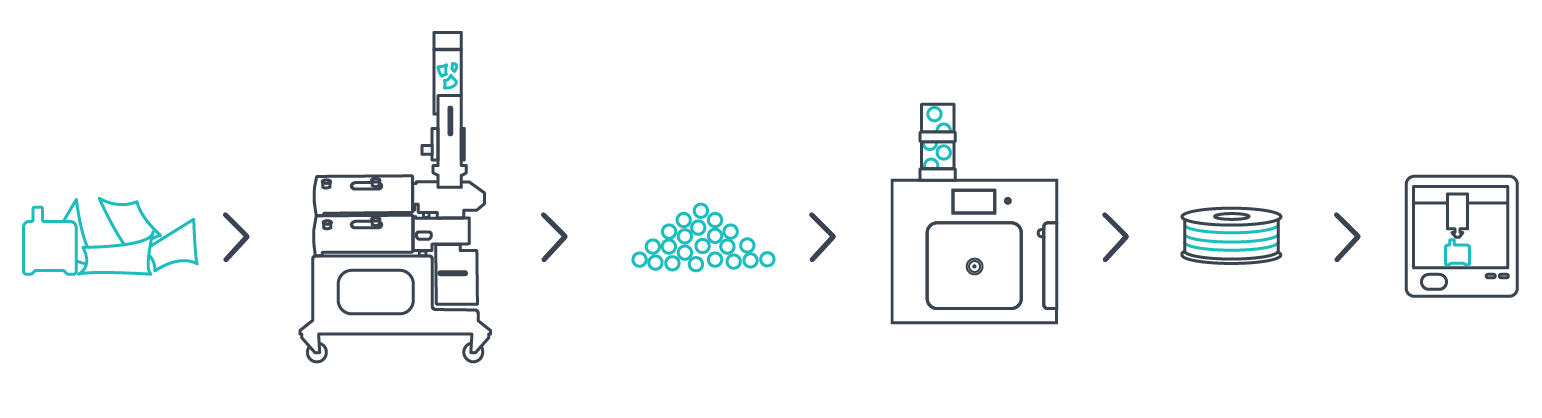
Extruding your own carbon fiber filament can be a rewarding process, offering customization and control over your filament properties. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to get you started, incorporating insights from our own extrusion process.
-
Preparation
Begin by gathering the necessary materials and equipment:
Carbon Fiber Composite Pellets: Choose a high-quality composite that blends carbon fibers with a thermoplastic base like PLA, ABS, or Nylon. It is important to consider the length of the fibers – we highly recommend fibers shorter than 0.5 mm (about 0.02 inches).
Filament Maker: 3devo Filament Makers are equipped with features suitable for handling carbon fiber composites, such as precise temperature control and consistent diameter monitoring.
Workspace: Set up a clean, well-ventilated workspace to avoid contamination and ensure safety.
Steps:
- Purge the Filament Maker to remove any residual material from previous runs – we have a comprehensive guide for the purging procedure available on our support platform.
- Preheat the machine to the desired temperature before loading the pellets – learn more about the Filament Maker’s Heaters here.
-
Loading the Filament Maker
Carefully load the carbon fiber composite pellets into the hopper of your filament maker.

-
Setting Parameters
Adjust the temperature and speed settings on your filament maker according to the specifications of your carbon fiber composite. Typically, carbon fiber composites require higher extrusion temperatures due to the thermal properties of the carbon fibers.
Key Parameters:
- Temperature: Set the extrusion temperature based on the thermoplastic base. For example, PLA composites might need around 200-230°C, while Nylon composites require higher temperatures, around 250-270°C.
- Speed: Adjust the extrusion speed to balance flow rate and cooling. Slower speeds can help maintain a consistent diameter and avoid air bubbles.
Steps:
- Refer to the material datasheet for specific temperature and speed recommendations.
- Begin with a slightly higher temperature setting (our Materials Specialists usually suggest 10% above melting temperature) and then gradually decreas as needed.
- Monitor the extrusion process closely and adjust parameters if you notice inconsistencies.
-
Extrusion
Start the extrusion process. As the pellets melt and pass through the nozzle, they will form a continuous filament. Ensure a consistent flow to avoid variations in filament diameter.
Suggestions:
- Monitor the extrusion nozzle to ensure a smooth, continuous filament emerges.
- Use the filament diameter monitoring system (3devo offers DevoVision, for example) to make real-time adjustments.
- Dependent on data shown via the monitoring system, adjust speed of the winder/puller wheel to ensure a consistent filament diameter.
-
Cooling and Spooling
Once the settings have been finetuned and the extrudate material is beginning to look like new filament, it’s time to begin the spooling process. Cut off the filament as close to the puller wheels as possible and guide it through both rings of the positioner. Remember to keep pulling on the filament to remain the tension on it.
Spooling Tips:
- Maintain a steady tension to avoid filament slack.
- Now the spool is building up tension, by rotating faster than it should. This makes sure the first few windings are tight. This typically takes two revolutions.
You are now on your way to creating a spool of new carbon fiber filament. We estimate that you’ll have one complete spool within 2.5 hours.
Troubleshooting Common Issues:
- Inconsistent Diameter: If the filament diameter varies, check the temperature and speed settings. Ensure the extrusion head is clean and free of blockages.
- Brittle Filament: This can result from over exposure to heat or incorrect temperature settings (usually too high rather than too low), and excessive additive percentage - too much carbon fiber and not enough polymer carrier, for example, can reduce the resistance of the compound to sheer stress. This can also be caused by an uneven distribution of carbon fiber within the polymer.
- Surface Imperfections: If the filament has a rough or uneven surface, ensure the pellets are clean and dry. This can also occur due to temperatures that are too low for the composite. You will be able to see unmelted particles on the surface of the filament.

Tips for Extruding Carbon Fiber Filament:
- Consistent Monitoring: Regularly monitor the extrusion process to ensure optimal performance and adjust parameters as needed. Look out for any inconsistencies in filament diameter or surface quality.
- Avoid Contamination: Keep the workspace and equipment clean to prevent impurities from affecting the filament quality. Any contamination can lead to defects in the final prints.
- Proper Storage: Store the extruded filament in a dry, cool place to maintain its properties and prevent moisture absorption. Use airtight containers with desiccants to control humidity.
By following the above steps and tips, you can produce high-quality carbon fiber filament tailored to your specific needs. 3devo’s Filament Makers are designed to achieve consistent, reliable results, unlocking new possibilities in 3D printing with carbon fiber materials.
Optimizing Your 3D Printing with Carbon Fiber Filament
In 3D printing, carbon fiber filament can be used in two forms: chopped fiber, which is mixed throughout the filament to provide enhanced strength and stiffness, and continuous fiber, which offers additional reinforcement for critical load-bearing applications. Both types are known for reducing the shrinkage and warping associated with high-temperature printing, making carbon fiber an excellent material for creating complex, durable parts.
Despite its many advantages, carbon fiber filament requires specific handling due to its abrasive nature. It can wear out standard nozzles quickly, so a hardened steel nozzle is recommended for printing. Additionally, the material's stiffness and fiber composition can lead to nozzle clogging if not managed properly. To overcome these challenges, maintaining optimal printing temperatures and using a direct drive extruder can help minimize issues and ensure high-quality prints.
When using carbon fiber filament for 3D printing, consider the following tips to achieve the best results:
- Nozzle Selection: Carbon fiber is abrasive and can wear down standard nozzles quickly. Use hardened steel or ruby-tipped nozzles for extended durability.
- Printing Speed and Temperature: Adjust your printer’s speed and temperature settings to match the filament’s requirements. Slower speeds and higher temperatures often yield better results.
- Bed Adhesion: Ensure good bed adhesion by using adhesives like glue stick or painter’s tape. A heated bed can also help in maintaining part stability.
- Post-Processing: Carbon fiber prints may have rough surfaces. Sanding or coating the final print can enhance the finish and aesthetic appeal.
Conclusion
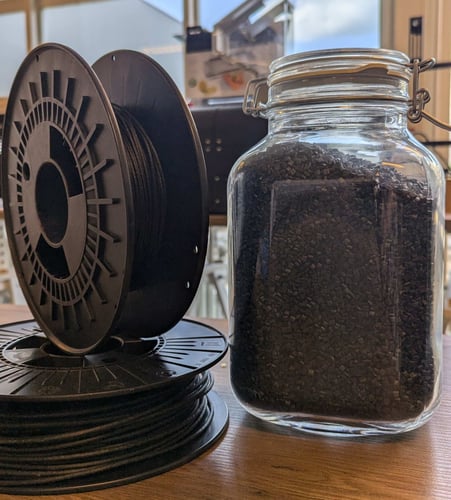

Carbon fiber filament opens up a new realm of possibilities in 3D printing, offering unparalleled strength, durability, and precision. By understanding the extrusion process and optimizing your printing techniques, you can harness the full potential of this advanced material. Whether you’re developing prototypes, manufacturing functional parts, or exploring innovative applications, carbon fiber filament is a game-changer.
-min.jpg?width=700&height=443&name=Sensor%20(1)-min.jpg)
Share this
- March 2025 (1)
- January 2025 (1)
- December 2024 (2)
- November 2024 (3)
- October 2024 (4)
- September 2024 (2)
- August 2024 (3)
- July 2024 (6)
- June 2024 (3)
- May 2024 (2)
- April 2024 (1)
- March 2024 (1)
- January 2024 (1)
- November 2023 (2)
- October 2023 (5)
- September 2023 (2)
- August 2023 (1)
- July 2023 (1)
- May 2023 (1)
- December 2022 (3)
- August 2022 (1)
- June 2022 (1)
- May 2022 (2)
- April 2022 (2)
- March 2022 (7)
- February 2022 (2)
- January 2022 (3)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (3)
- October 2021 (2)
- September 2021 (3)
- August 2021 (3)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (1)
- March 2021 (1)
- October 2020 (1)
- June 2020 (1)
- May 2020 (1)
- April 2020 (4)
- November 2019 (1)
- July 2019 (2)
- June 2019 (1)
- May 2019 (1)
- March 2019 (1)
- November 2018 (1)
- September 2018 (1)
- January 2018 (1)
- October 2017 (1)
- September 2017 (1)
- July 2017 (1)
- June 2017 (1)
- May 2017 (1)
- January 2017 (1)
- December 2016 (3)
- November 2016 (2)
- October 2016 (1)
- May 2016 (2)
- August 2015 (2)
- July 2015 (1)