Share this
ABS vs PLA Filament: A Comprehensive Guide
by 3devo on Jul 10, 2024 11:00:00 AM

In the exciting world of 3D printing, one of the first decisions you’ll need to make is choosing the right filament. This decision can be daunting for newcomers and seasoned enthusiasts alike, given the vast array of filament types available. However, two filaments that stand out in popularity are ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) and PLA (Polylactic Acid). These two materials have distinct properties, making them suitable for different applications. This guide will give a 3D printing filament comparison, helping you understand the key differences, benefits, and applications of ABS and PLA filaments, so you can make an informed decision for your 3D printing projects.
Understanding 3D Printing Filament
Before diving into the specifics of ABS and PLA, it's essential to understand the fundamental role of 3D printing filament. 3D printers don't just emit models right there on the spot; some material must be used to make a model colorful, strong, heavy, or whatever else you may need it for. This material is called the filament, and it is the ingredient used in your gourmet 3D-printed sandwich - 3D printing filament properties are fundamental when considering the application of your print. Its formal definition is a slender threadlike object or fiber from animal or plant-like structures. However, in 3D printing, it relates to the cable-like material that gets placed in a coil (or spool) onto a 3D printer. You can buy filament from stores, online, or even create your own with a Filament Extruder.
The Battle of the Titans: ABS vs PLA
There are several types of filaments available today, with new ones probably being released even as you read this article. However, the majority of these materials may not be relevant to your needs. Therefore, this guide will compare the two most popular thermoplastics, ABS and PLA, and understand why they are so appealing.
In the exciting world of 3D printing, ABS and PLA are the two most popular materials for a reason. They are relatively easy to work with, widely available, and suitable for a variety of applications.
ABS: The Robust Veteran
ABS, the granddaddy of filaments, is renowned for its strong build and slight flexibility. This makes it suitable for a variety of objects, from tools to toys, phone cases to fan blades. Its overall ease of extrusion, higher temperature resistance, improved flexibility, and strength make it a favored material for engineers and professional applications.
Pros of ABS:
- Very Sturdy and Hard: Suitable for machine parts and increased lifespan.
- More Flexible: Easier to work with for parts that need a bit of give.
- Higher Melting Point: Suitable for objects that need to cope with temperatures over 60ºC.
Cons of ABS:
- More Difficult to Print: Requires a heatbed and is prone to cracking if cooled too quickly.
- Not Food Safe: Not suitable for use with food.
- Odor: Produces a hot, burning plastic smell during printing.
PLA: The Environmentally-Friendly Choice
PLA, on the other hand, is derived from corn and other renewable starches, making it a biodegradable and environmentally friendly option. Its glossy appearance, large color variety, and different transparency choices make it an ideal choice for hobbyists and printing enthusiasts.
Pros of PLA:
- Environmentally Friendly: Biodegradable and made from renewable resources.
- Ease of Printing: Can be printed on a cold surface, has a shinier and smoother appearance, and allows for higher 3D printer speed.
- More Rigid: Suitable for applications requiring more rigid features and detail.
Cons of PLA:
- Can Deform Due to Heat: Not suitable for objects used in temperatures greater than 60ºC.
- Limited Flexibility: PLA is more rigid and brittle than ABS, making it less suitable for flexible parts.
- Color Alteration: The bent area of PLA can turn white, which might not be aesthetically pleasing for some applications.
Material Characteristics
It is crucial to understand the characteristics of ABS and PLA to choose the right material for your project. ABS has a higher glass transition temperature, which means it can withstand higher temperatures before it begins to deform. This characteristic makes it suitable for objects that will be exposed to high temperatures. However, PLA has a lower glass transition temperature, which means it will start to deform at lower temperatures than ABS.
On the other hand, PLA has a higher tensile strength than ABS, making it stronger and more rigid. However, this rigidity can also make it more brittle and less flexible than ABS. ABS has better ductility, which means it can deform under stress without breaking. This property makes ABS a better choice for objects under mechanical stress or requiring flexibility.
Printing Parameters
The printing parameters for ABS and PLA are also different. ABS requires a higher printing temperature compared to PLA. It typically prints at around 210-250°C, whereas PLA prints at around 160-220°C. The bed temperature for ABS also needs to be higher, usually around 100-110°C, to prevent warping, whereas PLA can be printed on a bed heated to around 50-60°C. Additionally, ABS tends to shrink as it cools, which can lead to warping or layer separation if not properly managed. PLA, on the other hand, has minimal shrinkage and is less prone to warping.
Moreover, ABS produces fumes during printing that can be unpleasant and may require proper ventilation, while PLA emits a sweet, corn-like smell and does not produce toxic fumes.
Recycling and Environmental Impact
PLA is biodegradable and compostable, making it an environmentally friendly option. However, it is important to note that PLA requires specific conditions to biodegrade fully, and it may not break down in a regular compost pile or landfill. ABS, on the other hand, is not biodegradable but can be recycled. However, the recycling process for ABS can be complex and is not widely available.
Moreover, the production of PLA consumes less energy and produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to ABS, making it a more sustainable option overall.
ABS vs PLA: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Pros and Cons ABS VS PLA Summary
We can’t tell you which one you should use, as we don’t know what you are going to be printing. But we can help you lean in the right direction by providing you with the pros and cons for each one. If you really enjoy the pros and can deal with the cons, then that filament is your answer.
ABS Pros:
- Very sturdy and durable
- More flexible - easier to work with
- Suitable for machine parts
- Increased lifespan
- Higher melting point
ABS Cons:
- More difficult to print
- Heatbed required
- Prone to cracking if cooled too quickly
- Not suitable for use with food
- Unpleasant smell
PLA Pros:
- Can be printed on a cold surface, heatbed not necessary
- Shiny, smooth appearance
- Prints faster
- More rigid features
- Can print higher detail
- Translucent colors
- Pleasant smell
PLA Cons:
- Can deform due to heat
- Less sturdy, more brittle
- Bent areas turn white
- Not suitable for use with food
- Lower melting point
When to Use Which Filament
Now that you are aware of the details of each type of filament and how it makes it either good or bad to use for certain conditions, it's time to decide when you should use ABS or PLA.
ABS
ABS is your go-to filament if the object you are printing is likely to be dropped often, like tool parts, or if the object needs to withstand temperatures over 60ºC. However, you should steer clear of ABS if you don’t have a heat bed, as this is essential for printing with ABS. Additionally, if you plan to print large objects in a place where there might be wind or changes in temperature, ABS might not be the best choice as it is prone to cracking and splitting in these conditions. Finally, if the place where you are printing doesn’t have good ventilation, it is better to avoid ABS as the smell produced during printing can get quite unpleasant.
PLA
PLA is the filament of choice for 3D printing enthusiasts and is suitable for a wide range of applications. It can sometimes be used in outdoor areas and is perfect for gifts and prototypes. However, PLA is not ideal for objects that might be dropped often as it is too brittle for tool handles. Also, if the object you are printing will be used in temperatures greater than 60ºC, it is better to avoid PLA as sagging can occur.
Cost Considerations
Cost is another essential factor to consider when choosing between ABS and PLA. The price of filament can vary based on the brand, quality, and the supplier. Generally, PLA is slightly more expensive than ABS because it is made from renewable resources, whereas ABS is made from petroleum. As of this article, the cost for ABS ranges from $14-60 per kg (€11.90 - 51/€kg), while PLA ranges from $19-75 per kg (€16.15 - 63.75/€kg). However, it is crucial to note that the price of filament does not always correlate with its quality. A more economical and empowering solution is to create your own filament using a Filament Extruder like the ones offered by 3devo. Our filament makers allow you to produce your own high-quality filament at a fraction of the cost of pre-made filaments, giving you greater control over the quality, color, and material properties. While purchasing filament from reputable suppliers is always an option, we highly recommend creating your own filament to maximize cost savings, customization, and environmental considerations.
Conclusion
Choosing between ABS and PLA involves weighing the pros and cons of each material against your specific needs and applications. ABS offers durability and flexibility, making it ideal for objects requiring strength and resilience. PLA, an eco-friendly alternative, offers a glossy finish and is well-suited for decorative items and prototypes. Before making a final decision, it is wise to consider each material's strengths and limitations and test small quantities of both. Additionally, producing your own filament using a Filament Maker, like those provided by 3devo, can offer cost savings, customization, and environmental benefits. This approach allows you to have greater control over the quality, color, and material properties, enabling you to optimize your 3D printing projects further.
FAQ
Producing PLA or ABS filament using a filament maker can present challenges like maintaining a consistent diameter and ensuring the filament is free of bubbles or voids. Temperature control is critical, as too high a temperature can degrade the material, and too low a temperature can lead to incomplete melting and inconsistent filament.
Produce Your Own ABS or PLA Filament?
Gain control, save costs, and customize your 3D prints by producing your own ABS or PLA filament.

Read more about Materials
%20-%20instasize%20(2).png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(39)%20-%20instasize%20(2).png)
Polymer Pyramid
Navigate your way through our Polymer Pyramid and discover the right materials for your needs.
Choose the Right Material
Unlock success in 3D printing by checking out our material selection guide now!
%20-%20instasize%20(1).png?width=800&height=640&name=PETG-e1494958102567%20(1)%20-%20instasize%20(1).png)
Unlock the Power of PET Plastic
Recycle your PET plastic by reading our Ultimate Guide to PET Plastic now!
Share this
- November 2025 (1)
- October 2025 (1)
- March 2025 (1)
- January 2025 (1)
- December 2024 (2)
- November 2024 (2)
- October 2024 (4)
- September 2024 (2)
- August 2024 (3)
- July 2024 (6)
- June 2024 (3)
- May 2024 (2)
- April 2024 (1)
- March 2024 (1)
- January 2024 (1)
- November 2023 (2)
- October 2023 (5)
- September 2023 (2)
- August 2023 (1)
- July 2023 (1)
- May 2023 (1)
- December 2022 (2)
- June 2022 (1)
- May 2022 (2)
- April 2022 (2)
- March 2022 (6)
- February 2022 (2)
- January 2022 (3)
- December 2021 (3)
- November 2021 (3)
- October 2021 (2)
- September 2021 (3)
- August 2021 (3)
- July 2021 (2)
- June 2021 (1)
- March 2021 (1)
- October 2020 (1)
- June 2020 (1)
- May 2020 (1)
- April 2020 (4)
- November 2019 (1)
- July 2019 (2)
- June 2019 (1)
- May 2019 (1)
- March 2019 (1)
- November 2018 (1)
- September 2018 (1)
- January 2018 (1)
- October 2017 (1)
- September 2017 (1)
- July 2017 (1)
- June 2017 (1)
- May 2017 (1)
- January 2017 (1)
- December 2016 (3)
- November 2016 (2)
- October 2016 (1)
- May 2016 (2)
- August 2015 (2)
- July 2015 (1)
%20-%20instasize.png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(35)%20-%20instasize.png)
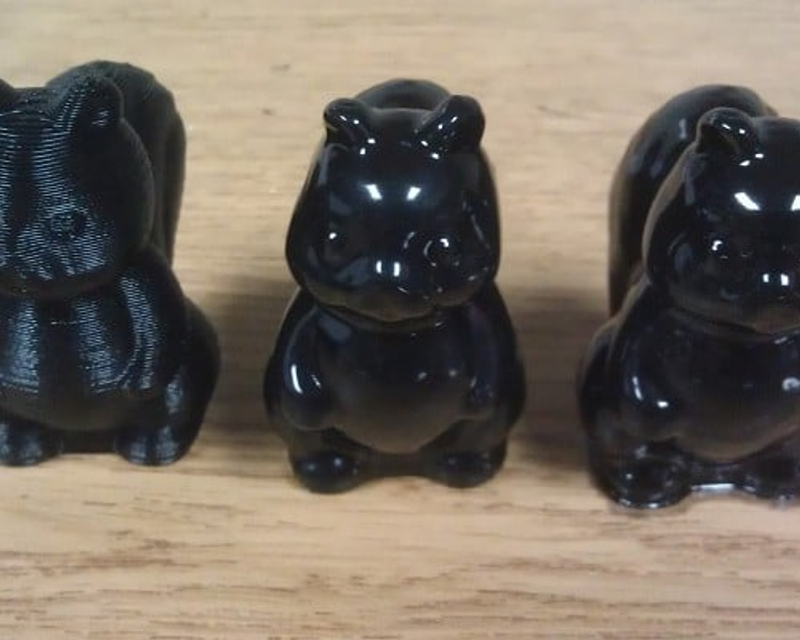


%20-%20instasize.png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(40)%20-%20instasize.png)
%20-%20instasize%20(1).png?width=800&height=640&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(42)%20-%20instasize%20(1).png)
